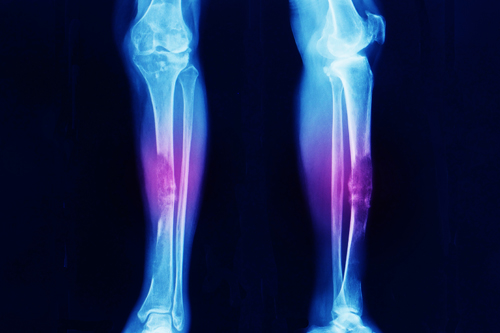
Bone Tumor
Bone Tumors
Bone Tumors are masses formed by abnormal cell growth in bones. They can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors, like osteochondromas, nonossifying fibromas, and enchondromas, are usually not fatal but may require treatment if they cause issues. Malignant tumors, like osteosarcoma, are cancerous and may spread through the body. Causes are largely unknown but may include genetics, radiation, injuries, or rapid bone growth.
Symptoms of bone tumors include a persistent bone ache, severe pain during activity or at night, swelling, pathologic fractures, or an unexpected mass. Malignant tumors may also cause night sweats or fever.
Diagnosis involves a combination of methods:
- Physical Exam: Evaluating tenderness and range of motion.
- Blood Tests: Including alkaline phosphatase to check bone activity.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and bone scans to locate and assess tumors.
- Biopsies: A sample of tumor tissue is removed and examined. Types include:
Needle Biopsy: A small sample is taken using a needle guided by imaging.
Incisional (Open) Biopsy: A surgical procedure under anesthesia to remove tissue for analysis.
Timely diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and to rule out other conditions.